The 25th anniversary of China Optical Expo is underway -- Bai-link Communications is making progress together

The 25th anniversary of China Optical Expo is underway -- Bai-link Communications is making progress together
Thank you for your trust and support for Bai-link! Bai-link is based on the most reliable product quality, the most thoughtful service,
View more >
When you purchase Bai-link products, Bai-link technical service department will provide you with detailed product principle introduction,
View more >
Common problems encountered when using Bai-link OLT, ONU optical cat, PoE ONU, switch and other communication devices, and...
View more >
There is no relevant version of firmware download yet! Please pay attention to our website in the future. Firmware updates for relevant...
View more >
Bai-link focuses on providing the public with the best high-quality, high-performance and cost-effective optical fiber communication equipment PON, switches, wireless coverage and other solutions.
View more >
Bai-link is a leading manufacturer of engineering network communication equipment. We believe that integrity is the foundation of all cooperation, tolerance is the prerequisite for solving problems, ...
View more >
Welcome to join the Bai link communication company family, let's create miracles together. Our team is stronger because of you, and we welcome you to become a member of it。
View more >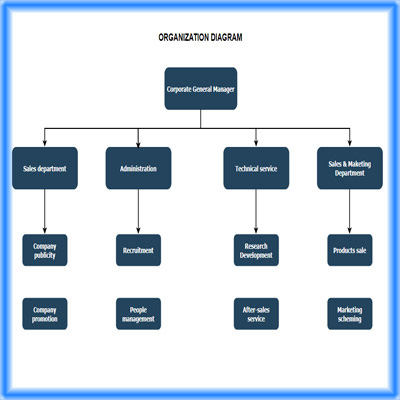
Bai-link® (Shenzhen) Communication Technology Co., Ltd. has a general manager's office and four departments under the organizational framework, namely: Business Department, ...
View more >
The 25th anniversary of China Optical Expo is underway -- Bai-link Communications is making progress together